An Introduction to the Business Model Canvas Methodology
When you are in the process of becoming an entrepreneur, one of the most important tasks that you can perform is transitioning your ideas from an intangible format to a tangible composition. In this way, you can communicate your ideas clearly to others. Previously, this meant that you would have to spend several weeks to a couple of months conceptualizing, researching, drafting, revising, and packaging a full twenty-plus-page business plan. That model is finding its way out of the door for a few reasons.
Silicon Valley berthed the idea of quick software updates and iterations. The goal is to program quickly and make adjustments as needed based on the feedback provided by users. Fundamentally, this method reduces waste and improves processes, inventory, and time. It’s a faster way to get ideas out of your head and into action. “Lean” is used to express this methodology. A Lean Model Canvas is divided into nine blocks that help you focus on the most strategically important elements of your business idea. This document is prepared to be used as a visual representation of what is needed to start or maintain business success. Each step summarized how your idea should operate based on the information that you have on hand. It’s a living document that is to be updated easily, and as needed.
A business model canvas contains the following categories to help pinpoint the answers important questions about your concept:
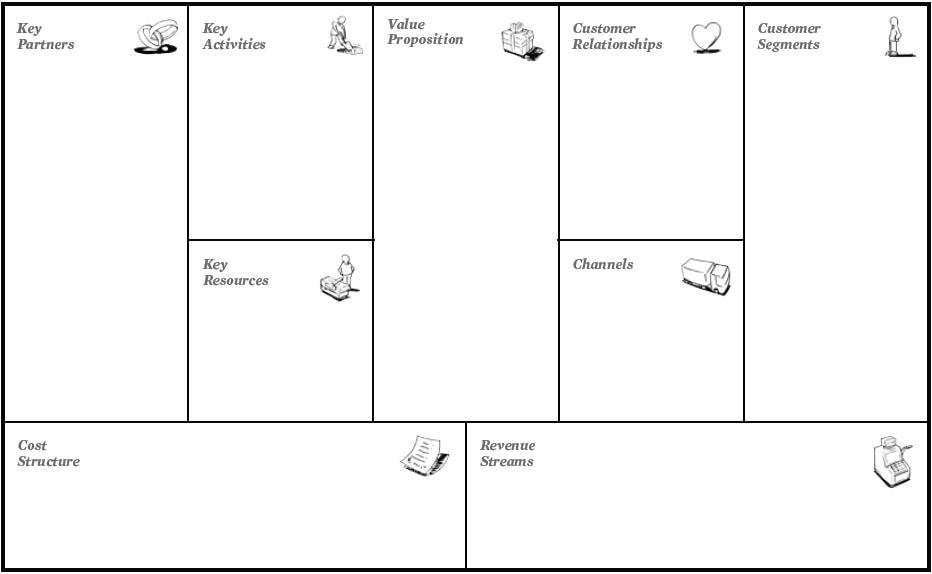
- Key Partners
- Who are our key partners?
- Who are our key suppliers?
- Which key resources are we acquiring from partners?
- Which key activities do partners perform?
- Key Activities
- What key activities do our value propositions require our distribution channels, customer relationships, or revenue streams?
- Key Resources
- What key resources do our value propositions require our distribution channels, customer relationships, or revenue streams?
- Value Proposition
- What value do we deliver to the customer?
- Which one of our customer’s problems are we helping to solve?
- What bundles of products and services are we offering to each customer segment?
- Which customer needs are we satisfying?
- Customer Relationships
- What type of relationship does each of our customer segments expect us to establish with them?
- Which ones have we already established?
- How are they integrated with the rest of our business model?
- How costly are they?
- Channels
- Through which channels do our customer segments want to be reached?
- How are we reaching them now?
- How are our channels integrated?
- Which ones work best?
- Which ones are most cost-efficient?
- How are we integrating them with customer routines?
- Customer Segments
- Who are we creating value for?
- Who are our most important customers?
- Cost Structure
- What are the most important costs inherent to our business model?
- Which key resources are most expensive?
- Which key activities are most expensive?
- Revenue Streams
- For what value are our customer really willing to pay?
- For what do they currently pay?
- How are they currently paying?
- How would they prefer to pay?
- How much does each revenue stream contribute to overall revenue?
Step-by-step guide
- Investigation
You can learn about an industry by looking at your competitors. Start by selecting from competitors in your space and map out their business models. With this information you’ll have a deeper insight into what customers want and are willing to pay for. This will give you clear understanding of what is happening across the industry and not just in your business. Additionally, you’ll be able to discover important information that have helped other businesses become successful in their market. - Initiation
Start by mapping out your idea or business by writing out the most important aspects. Make your list and criteria as clear as you can. Make sure that others can understand your idea if you were to explain what the criteria means three months later. Also, try not mix future ideas with current ideas. - Integration
Initially, you want to brainstorm and spitball as many ideas as possible on paper. Afterwhich, you want to link the blocks together, so that the content corresponds with each of the other blocks in the business model canvas. If you have multiple customer segments, you will want to choose a color for each of the segments. This allows you to visualize if the customer segments connect to the value proposition and the revenue steam. - Examination
Take a short break. When you come back ask yourself if you forgot anything. Check to make sure that every segmentation links to a value proposition and a revenue stream. Moreover, make sure that both sides of the canvas support each other. If it doesn’t support, it can be removed from the canvas.
The primary idea here is to spend an hour or less jotting down the idea. Either print out, use a whiteboard, or jot down on a piece of paper to fill out a business model canvas. After a while, you’ll be able to piece everything together mentally, and write down your idea into a notebook.
Once you have your Business Model Canvas written down, it’s time to test it. Try many and multiple iterations, even if it isn’t a Silicon Valley tech company. Continue to test each one after the other to determine which business model is the best. It might sound like a lot of work, but you’ll become accustomed to thinking in this way. The worst thing an entrepreneur can do is build a something that no body wants; this will save you time, money, and energy.
It’s your job as an entrepreneur to solve problems by getting your ideas into people’s hands. Traditional business plans do have a purpose, but they are not relevant in this stage. For ideation, they consume too much time and have not been validated. They are more suited for businesses that are running and are looking for investment. During the ideation stage, create a business model canvas, get your ideas down, stay lean, test your hypothesis, and start building.
Read this article if you need help with generating business ideas!

